【Spring Security】 拦截器
【Spring Security】 拦截器
Metadata
title: 【Spring Security】 拦截器
date: 2023-02-03 10:50
tags:
- 行动阶段/完成
- 主题场景/组件
- 笔记空间/KnowladgeSpace/ProgramSpace/ModuleSpace
- 细化主题/Module/SpringSecurity
categories:
- SpringSecurity
keywords:
- SpringSecurity
description: 【Spring Security】 拦截器
【Spring Security】 拦截器
Security 中有各种各样的过滤器,也存在着拦截器,比如 MethodSecurityInterceptor。
**过滤器 (Filter)**:它依赖于 servlet 容器。在实现上,基于函数回调,它可以对几乎所有请求进行过滤。
拦截器(Interceptor):拦截器(Interceptor)是基于 Java 的[[../../../BasicsSpace/Language/Java/Java 基础/【Java 基础】 反射|反射机制]],比如 Spring 中的 AOP,可以对方法运行时进行拦截增强。
MethodInterceptor
MethodInterceptor 接口位于 spring [[../../../SpringSpace/SpringFramework/Spring 面向切面 AOP|aop]] 包下。顾名思义,是一个方法拦截器,在调用目标对象的方法时,就可以实现在调用方法之前、调用方法过程中、调用方法之后对其进行控制。
也可以使用 @Aspect 注解来实现。
入门示例
undefined
AbstractSecurityInterceptor
AbstractSecurityInterceptor 是一个抽象类,注释说这是受保护对象实现安全拦截的抽象类,顾名思义,是对未放行资源保护的拦截器。
成员属性
可以看出,AbstractSecurityInterceptor 维护了很多管理器,用于保护资源。
// Spring MessageSource访问
protected MessageSourceAccessor messages = SpringSecurityMessageSource.getAccessor();
// 时间发布器
private ApplicationEventPublisher eventPublisher;
// 鉴权管理器
private AccessDecisionManager accessDecisionManager;
// 后置处理器
private AfterInvocationManager afterInvocationManager;
// 认证管理器
private AuthenticationManager authenticationManager = new NoOpAuthenticationManager();
// 当前访问对象管理器,用于创建临时的Authentication对象
private RunAsManager runAsManager = new NullRunAsManager();
// 是否重新认证
private boolean alwaysReauthenticate = false;
// 是否拒绝公共调用
private boolean rejectPublicInvocations = false;
// 是否验证配置属性
private boolean validateConfigAttributes = true;
// 是否发布发布授权成功
private boolean publishAuthorizationSuccess = false;
核心方法
既然是拦截器,那么肯定提供了前置和后置方法,前置校验当前请求是否合法,进行授权判断,拒绝后抛出异常,通过后,执行请求,并最终执行后置方法。
由于这个一个抽象类,肯定只定义的一些逻辑方法,具体执行都是子类去调用的。
可以看到,在前置方法中,会进行授权判断,未通过,抛出 AccessDeniedException,被 ExceptionTranslationFilter 捕获并处理。
/**
* 获取权限信息并进行授权判断,
*/
protected InterceptorStatusToken beforeInvocation(Object object) {
Assert.notNull(object, "Object was null");
// 1. 判断object是不是FilterInvocation
if (!getSecureObjectClass().isAssignableFrom(object.getClass())) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Security invocation attempted for object " + object.getClass().getName()
+ " but AbstractSecurityInterceptor only configured to support secure objects of type: "
+ getSecureObjectClass());
}
// 2. 获取配置的访问控制规则 any request =》authenticated ,没有配置,return null
Collection<ConfigAttribute> attributes = this.obtainSecurityMetadataSource().getAttributes(object);
if (CollectionUtils.isEmpty(attributes)) {
Assert.isTrue(!this.rejectPublicInvocations,
() -> "Secure object invocation " + object
+ " was denied as public invocations are not allowed via this interceptor. "
+ "This indicates a configuration error because the "
+ "rejectPublicInvocations property is set to 'true'");
if (this.logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
this.logger.debug(LogMessage.format("Authorized public object %s", object));
}
publishEvent(new PublicInvocationEvent(object));
return null; // no further work post-invocation
}
// 3. 判断认证对象Authentication是否为null
if (SecurityContextHolder.getContext().getAuthentication() == null) {
credentialsNotFound(this.messages.getMessage("AbstractSecurityInterceptor.authenticationNotFound",
"An Authentication object was not found in the SecurityContext"), object, attributes);
}
// 4. 获取Authentication对象
Authentication authenticated = authenticateIfRequired();
if (this.logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
this.logger.trace(LogMessage.format("Authorizing %s with attributes %s", object, attributes));
}
// Attempt authorization
// 5. 进行授权判断
attemptAuthorization(object, attributes, authenticated);
if (this.logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
this.logger.debug(LogMessage.format("Authorized %s with attributes %s", object, attributes));
}
// 6. 发布授权成功
if (this.publishAuthorizationSuccess) {
publishEvent(new AuthorizedEvent(object, attributes, authenticated));
}
// Attempt to run as a different user
// 7. 对Authentication进行再处理,这里没有处理,直接返回null
Authentication runAs = this.runAsManager.buildRunAs(authenticated, object, attributes);
if (runAs != null) {
SecurityContext origCtx = SecurityContextHolder.getContext();
SecurityContextHolder.setContext(SecurityContextHolder.createEmptyContext());
SecurityContextHolder.getContext().setAuthentication(runAs);
if (this.logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
this.logger.debug(LogMessage.format("Switched to RunAs authentication %s", runAs));
}
// need to revert to token.Authenticated post-invocation
return new InterceptorStatusToken(origCtx, true, attributes, object);
}
this.logger.trace("Did not switch RunAs authentication since RunAsManager returned null");
// no further work post-invocation
// 8. 返回InterceptorStatusToken
return new InterceptorStatusToken(SecurityContextHolder.getContext(), false, attributes, object);
}
后置处理器,主要用于对结果集进行处理。
/**
* 后置处理,可以对受保护对象返回的结果进行处理
* @param token beforeInvocation 返回拦截处理信息对象
* @param returnedObject 方法执行后 调用返回的任何对象
* @return 返回结果集
*/
protected Object afterInvocation(InterceptorStatusToken token, Object returnedObject) {
// 1. token为null. 直接返回结果集
if (token == null) {
// public object
return returnedObject;
}
finallyInvocation(token); // continue to clean in this method for passivity
if (this.afterInvocationManager != null) {
// Attempt after invocation handling
try {
// 2. 调用后置处理器,处理结果集
returnedObject = this.afterInvocationManager.decide(token.getSecurityContext().getAuthentication(),
token.getSecureObject(), token.getAttributes(), returnedObject);
} catch (AccessDeniedException ex) {
// 3. 有异常直接抛出
publishEvent(new AuthorizationFailureEvent(token.getSecureObject(), token.getAttributes(),
token.getSecurityContext().getAuthentication(), ex));
throw ex;
}
}
return returnedObject;
}
FilterSecurityInterceptor
FilterSecurityInterceptor 是 AbstractSecurityInterceptor 的其中一个子类。虽然继承了拦截器,又实现了 Filter 接口,实际还是一个过滤器,只是调用了拦截器中的相关方法。
源码注释中说这是一个,实现通过过滤器实现对 HTTP 资源进行安全处理的类。也就是说,这个拦截器拦截 HTTP 请求,进行拦截鉴权处理。
从拦截器链中看,它是最后一个过滤器。可以看做过滤器链的出口,根据资源权限配置来判断当前请求是否有权限访问对应的资源。如果访问受限会抛出相关异常,并由 ExceptionTranslationFilter 过滤器进行捕获和处理。
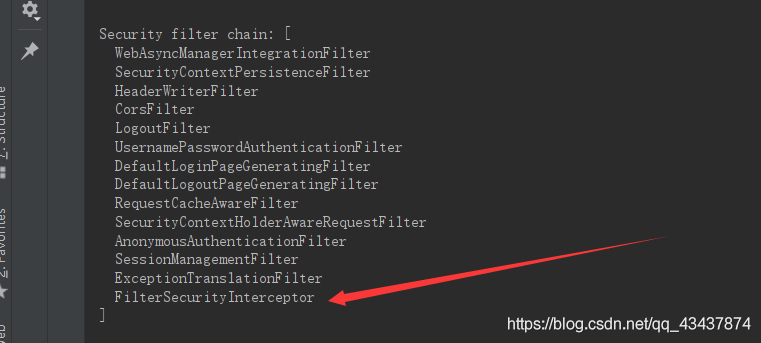
可以从它的 invoke 方法中看出,主要是调用了父类的方法进行前置鉴权、后置结果集处理。
/**
* doFilter实际执行的方法
* @param filterInvocation 封装了request response 过滤器链的对象
*/
public void invoke(FilterInvocation filterInvocation) throws IOException, ServletException {
// 1. 如果已经执行过该过滤器,直接放行
if (isApplied(filterInvocation) && this.observeOncePerRequest) {
// filter already applied to this request and user wants us to observe
// once-per-request handling, so don't re-do security checking
filterInvocation.getChain().doFilter(filterInvocation.getRequest(), filterInvocation.getResponse());
return;
}
// first time this request being called, so perform security checking
// 2. 第一次调用这个请求,所以执行安全检查
if (filterInvocation.getRequest() != null && this.observeOncePerRequest) {
// 3. 在request中添加__spring_security_filterSecurityInterceptor_filterApplied = true,表示执行了该过滤器
filterInvocation.getRequest().setAttribute(FILTER_APPLIED, Boolean.TRUE);
}
// 4. 前置访问控制处理
InterceptorStatusToken token = super.beforeInvocation(filterInvocation);
try {
// 5. 放行
filterInvocation.getChain().doFilter(filterInvocation.getRequest(), filterInvocation.getResponse());
} finally {
super.finallyInvocation(token);
}
// 6. 后置处理
super.afterInvocation(token, null);
}
MethodSecurityInterceptor
MethodSecurityInterceptor 也继承自 AbstractSecurityInterceptor,实现了 MethodInterceptor 接口。其功能也是对资源访问进行鉴权,那么和 FilterSecurityInterceptor 有什么区别呢?
一个是过滤器,一个是方法拦截器,所以他们的拦截对象是不同的,一个是拦截 Http 请求,一个是拦截方法执行。
在执行父类 beforeInvocation 方法时传入的参数是不一样的,FilterSecurityInterceptor 传入的是 FilterInvocation,MethodInterceptor 传入的是 MethodInvocation。
维护的 SecurityMetadataSource 不一样,SecurityMetadataSource 是存储和获取授权配置的接口,MethodSecurityInterceptor 中维护的是 MethodSecurityMetadataSource,FilterSecurityInterceptor 维护的是 FilterInvocationSecurityMetadataSource。
FilterInvocationSecurityMetadataSource 存放的是 HttpSecurity 配置类中配置的授权规则。FilterSecurityInterceptor 会从这里获取到这些规则,然后对其进行授权判断。
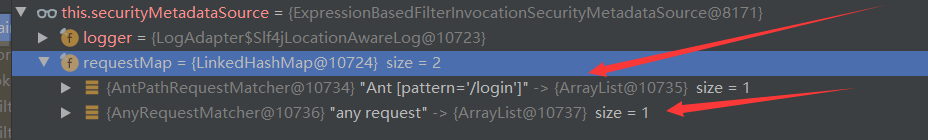
MethodSecurityMetadataSource 存放的是所以类和方法,会根据当前执行的类和方法,去内存中遍历,查询到当前执行方法配置的权限注解,然后对其进行授权判断。
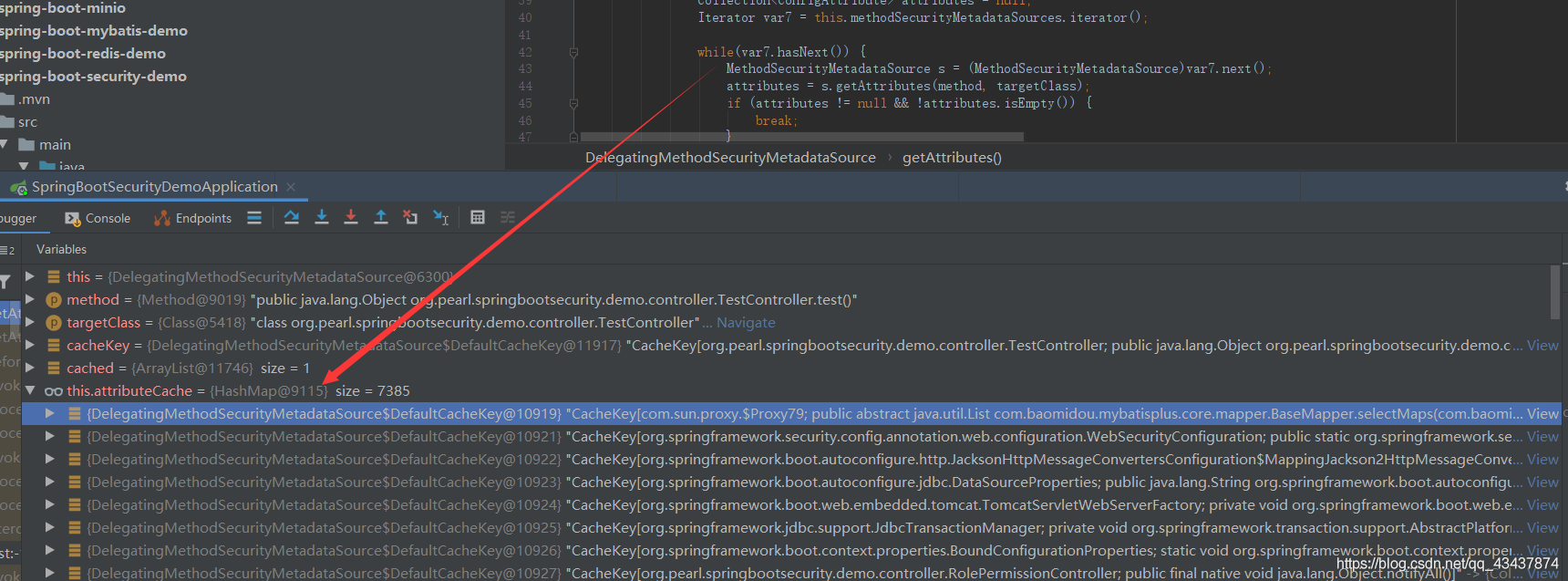
总结
由上可知,FilterSecurityInterceptor 是拦截请求,然后从配置类中获取缓存的授权规则,而 MethodSecurityInterceptor 是拦截方法,从缓存中查询当前方法配置的权限注解规则,然后都调用父类的前置、后置方法,进行授权判断处理。所以一次请求,会先执行 FilterSecurityInterceptor,然后再执行 MethodSecurityInterceptor。

