【Spring Security】 授权 流程分析
【Spring Security】 授权 流程分析
Metadata
title: 【Spring Security】 授权 流程分析
date: 2023-02-02 14:36
tags:
- 行动阶段/完成
- 主题场景/组件
- 笔记空间/KnowladgeSpace/ProgramSpace/ModuleSpace
- 细化主题/Module/SpringSecurity
categories:
- SpringSecurity
keywords:
- SpringSecurity
description: 【Spring Security】 授权 流程分析
【Spring Security】 授权 流程分析
1. 进入 ExceptionTranslationFilter
首先会进入 ExceptionTranslationFilter 的 doFilter 方法,之前说过这个过滤器的主要作用是拦截异常并处理。
private void doFilter(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, FilterChain chain)
throws IOException, ServletException {
try {
// 1. 请求直接放行
chain.doFilter(request, response);
} catch (IOException ex) {
throw ex;
} catch (Exception ex) {
// Try to extract a SpringSecurityException from the stacktrace
// 2. 捕获后续出现的异常
Throwable[] causeChain = this.throwableAnalyzer.determineCauseChain(ex);
RuntimeException securityException = (AuthenticationException) this.throwableAnalyzer
.getFirstThrowableOfType(AuthenticationException.class, causeChain);
if (securityException == null) {
securityException = (AccessDeniedException) this.throwableAnalyzer
.getFirstThrowableOfType(AccessDeniedException.class, causeChain);
}
if (securityException == null) {
rethrow(ex);
}
if (response.isCommitted()) {
throw new ServletException("Unable to handle the Spring Security Exception "
+ "because the response is already committed.", ex);
}
// 3. 处理发生的异常
handleSpringSecurityException(request, response, chain, securityException);
}
}
2. 进入 FilterSecurityInterceptor
接下来进入 FilterSecurityInterceptor 过滤器,他的 doFilter 方法,调用的是自身的 invoke(FilterInvocation filterInvocation) 方法。该方法完成了整个访问控制逻辑。
/**
* doFilter实际执行的方法
* @param filterInvocation 封装了request response 过滤器链的对象
*/
public void invoke(FilterInvocation filterInvocation) throws IOException, ServletException {
// 1. 如果已经执行过该过滤器,直接放行
if (isApplied(filterInvocation) && this.observeOncePerRequest) {
// filter already applied to this request and user wants us to observe
// once-per-request handling, so don't re-do security checking
filterInvocation.getChain().doFilter(filterInvocation.getRequest(), filterInvocation.getResponse());
return;
}
// first time this request being called, so perform security checking
// 2. 第一次调用这个请求,所以执行安全检查
if (filterInvocation.getRequest() != null && this.observeOncePerRequest) {
// 3. 在request中添加__spring_security_filterSecurityInterceptor_filterApplied = true,表示执行了该过滤器
filterInvocation.getRequest().setAttribute(FILTER_APPLIED, Boolean.TRUE);
}
// 4. 前置访问控制处理
InterceptorStatusToken token = super.beforeInvocation(filterInvocation);
try {
// 5. 放行 filterInvocation.getChain().doFilter(filterInvocation.getRequest(), filterInvocation.getResponse());
} finally {
super.finallyInvocation(token);
}
// 6. 后置处理
super.afterInvocation(token, null);
}
3. 进入 AbstractSecurityInterceptor
在 FilterSecurityInterceptor 中,会调用父类的 beforeInvocation(filterInvocation) 方法进行处理,最终返回一个 InterceptorStatusToken 对象,它就是 spring security 处理鉴权的入口。
protected InterceptorStatusToken beforeInvocation(Object object) {
Assert.notNull(object, "Object was null");
// 1. 判断object是不是FilterInvocation
if (!getSecureObjectClass().isAssignableFrom(object.getClass())) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Security invocation attempted for object " + object.getClass().getName()
+ " but AbstractSecurityInterceptor only configured to support secure objects of type: "
+ getSecureObjectClass());
}
// 2. 获取配置的访问控制规则 any request =》authenticated ,没有配置,return null
Collection<ConfigAttribute> attributes = this.obtainSecurityMetadataSource().getAttributes(object);
if (CollectionUtils.isEmpty(attributes)) {
Assert.isTrue(!this.rejectPublicInvocations,
() -> "Secure object invocation " + object
+ " was denied as public invocations are not allowed via this interceptor. "
+ "This indicates a configuration error because the "
+ "rejectPublicInvocations property is set to 'true'");
if (this.logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
this.logger.debug(LogMessage.format("Authorized public object %s", object));
}
publishEvent(new PublicInvocationEvent(object));
return null; // no further work post-invocation
}
// 3. 判断认证对象Authentication是否为null
if (SecurityContextHolder.getContext().getAuthentication() == null) {
credentialsNotFound(this.messages.getMessage("AbstractSecurityInterceptor.authenticationNotFound",
"An Authentication object was not found in the SecurityContext"), object, attributes);
}
// 4. 获取Authentication对象
Authentication authenticated = authenticateIfRequired();
if (this.logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
this.logger.trace(LogMessage.format("Authorizing %s with attributes %s", object, attributes));
}
// Attempt authorization
// 5. 进行授权判断
attemptAuthorization(object, attributes, authenticated);
if (this.logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
this.logger.debug(LogMessage.format("Authorized %s with attributes %s", object, attributes));
}
// 6. 发布授权成功
if (this.publishAuthorizationSuccess) {
publishEvent(new AuthorizedEvent(object, attributes, authenticated));
}
// Attempt to run as a different user
// 7. 对Authentication进行再处理,这里没有处理,直接返回null
Authentication runAs = this.runAsManager.buildRunAs(authenticated, object, attributes);
if (runAs != null) {
SecurityContext origCtx = SecurityContextHolder.getContext();
SecurityContextHolder.setContext(SecurityContextHolder.createEmptyContext());
SecurityContextHolder.getContext().setAuthentication(runAs);
if (this.logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
this.logger.debug(LogMessage.format("Switched to RunAs authentication %s", runAs));
}
// need to revert to token.Authenticated post-invocation
return new InterceptorStatusToken(origCtx, true, attributes, object);
}
this.logger.trace("Did not switch RunAs authentication since RunAsManager returned null");
// no further work post-invocation
// 8. 返回InterceptorStatusToken
return new InterceptorStatusToken(SecurityContextHolder.getContext(), false, attributes, object);
}
在 beforeInvocation 方法中的核心方法为 attemptAuthorization,它会调用授权管理器进行决策,当失败发生异常时,会爆出异常。
/**
* 授权判断
*
* @param object filter invocation [GET /test]
* @param attributes 配置的URL放行、需要验证路径等配置
* @param authenticated 认证对象
*/
private void attemptAuthorization(Object object, Collection<ConfigAttribute> attributes,
Authentication authenticated) {
try {
// 1. 调用授权管理器进行决策
this.accessDecisionManager.decide(authenticated, object, attributes);
} catch (AccessDeniedException ex) {
// 2. 访问被拒绝。抛出AccessDeniedException异常
if (this.logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
this.logger.trace(LogMessage.format("Failed to authorize %s with attributes %s using %s", object,
attributes, this.accessDecisionManager));
} else if (this.logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
this.logger.debug(LogMessage.format("Failed to authorize %s with attributes %s", object, attributes));
}
// 3. 发布授权失败事件
publishEvent(new AuthorizationFailureEvent(object, attributes, authenticated, ex));
throw ex;
}
}
4. 决策者进行投票
调用授权管理器进行决策,会进入默认的决策器 AffirmativeBased,上面说过它的投票机制,这里获取到的选民只有一个。
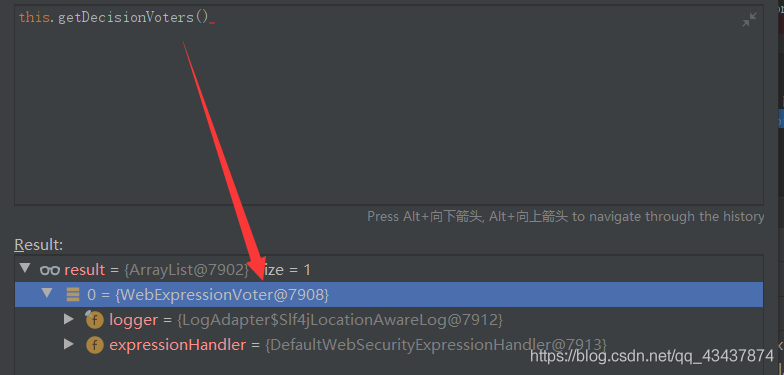
循环投票者,并开始计票。
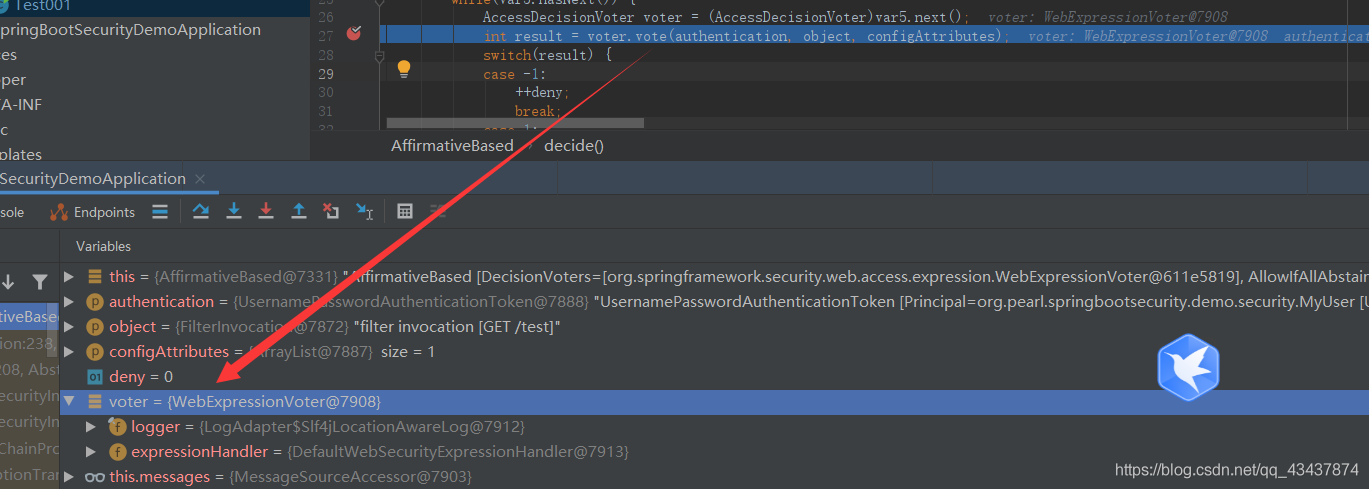
5. 开始投票
进入 WebExpressionVoter 的 vote 方法开始投票。
// 投票
@Override
public int vote(Authentication authentication, FilterInvocation filterInvocation,
Collection<ConfigAttribute> attributes) {
// 1. 校验参数
Assert.notNull(authentication, "authentication must not be null");
Assert.notNull(filterInvocation, "filterInvocation must not be null");
Assert.notNull(attributes, "attributes must not be null");
// 2. 获取http配置项
WebExpressionConfigAttribute webExpressionConfigAttribute = findConfigAttribute(attributes);
// 3. 没有配置规则,弃权
if (webExpressionConfigAttribute == null) {
this.logger
.trace("Abstained since did not find a config attribute of instance WebExpressionConfigAttribute");
return ACCESS_ABSTAIN;
}
// 4. 对EL表达式进行处理
EvaluationContext ctx = webExpressionConfigAttribute.postProcess(
this.expressionHandler.createEvaluationContext(authentication, filterInvocation), filterInvocation);
boolean granted = ExpressionUtils.evaluateAsBoolean(webExpressionConfigAttribute.getAuthorizeExpression(), ctx);
if (granted) {
// 5. 符合条件,赞成票
return ACCESS_GRANTED;
}
this.logger.trace("Voted to deny authorization");
// 6. 最后都没有则反对票
return ACCESS_DENIED;
}
6. 对表达式进行处理
投票中的核心代码为:
EvaluationContext ctx = webExpressionConfigAttribute.postProcess(this.expressionHandler.createEvaluationContext(authentication, filterInvocation), filterInvocation);
boolean granted = ExpressionUtils.evaluateAsBoolean(webExpressionConfigAttribute.getAuthorizeExpression(), ctx);
首先会创建 EL 表达式的上下文。
this.expressionHandler.createEvaluationContext(authentication, filterInvocation)
然后调用 ExpressionUtils 工具类对 EL 表达式进行处理,最终调用的是 SpelExpression 中的 getValue 方法。
第一次是对配置类中的规则进行校验,这里是 anyRequest()).authenticated(),因为登录了,所以这个投票是通过的。
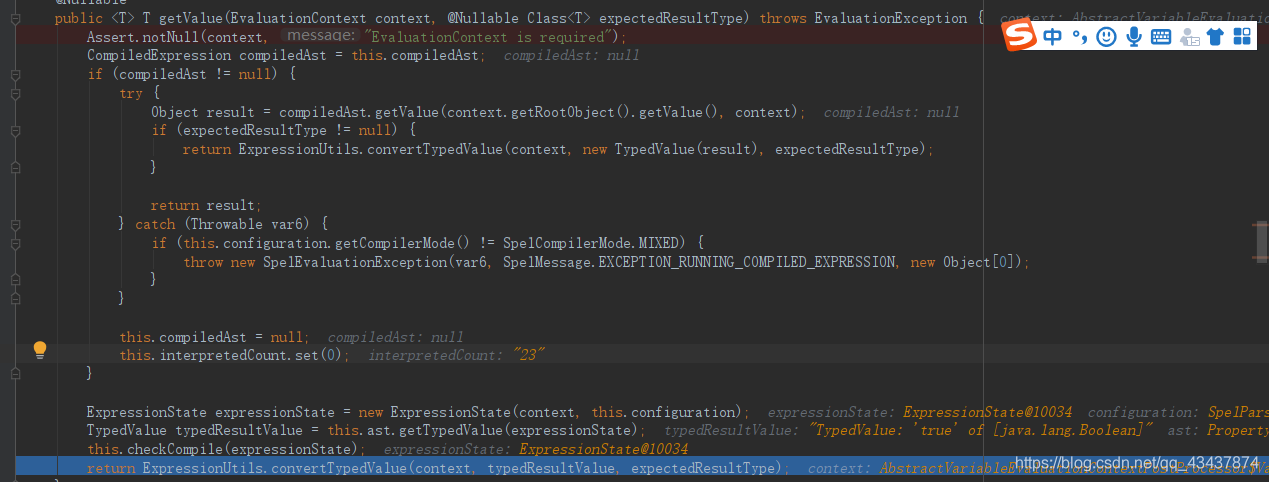
第二次是对我们配置了权限注解的方法进行校验。
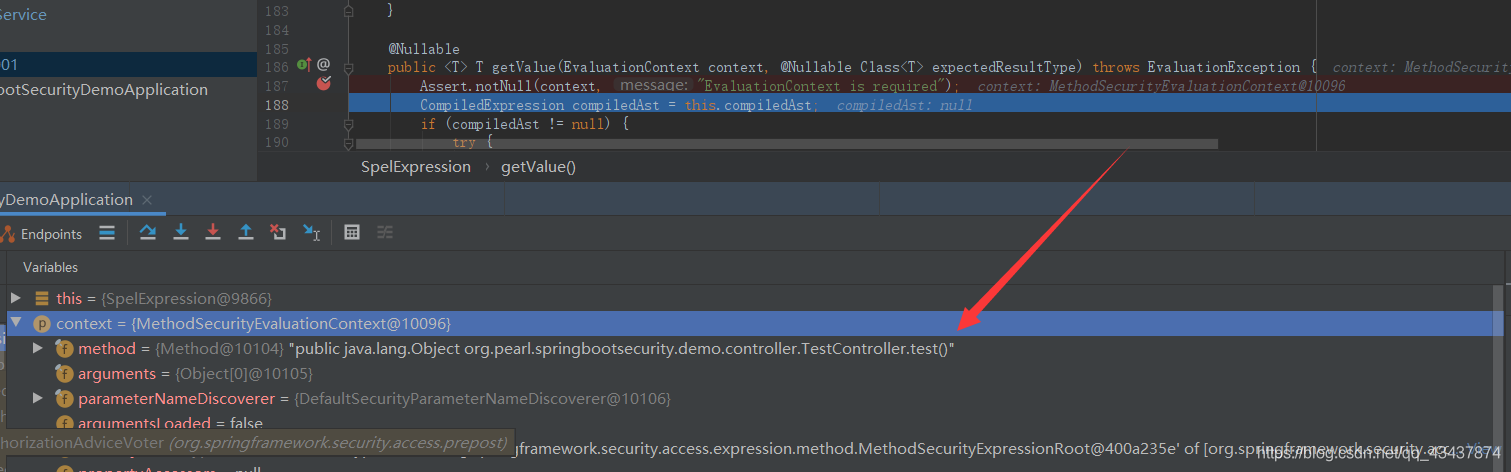
会首先获取到我们请求方法上的 EL 表达式,然后进行配置校验,涉及到 EL 的相关知识,这里后续介绍。
表达式检验之后,这个当前用户有这个角色,所以投票通过,加下来就要进行授权成功处理了。
7. 授权成功处理
没有抛出异常,则认为授权通过,FilterSecurityInterceptor 会进入 finallyInvocation 方法。这个方法主要是判断需不需要重新设置 SecurityContext 内容,这里没有配置,直接跳过。
protected void finallyInvocation(InterceptorStatusToken token) {
if (token != null && token.isContextHolderRefreshRequired()) {
SecurityContextHolder.setContext(token.getSecurityContext());
if (this.logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
this.logger.debug(LogMessage.of(() -> {
return "Reverted to original authentication " + token.getSecurityContext().getAuthentication();
}));
}
}
}
接下来进入后置处理 afterInvocation 方法,再次调用了 finallyInvocation 方法,然后查询是否还有决策后置处理器,如果有,再次进行决策。最后的最后,才代表授权成功,就交由 Spring MVC , 访问到我们的 controller 方法了。
protected Object afterInvocation(InterceptorStatusToken token, Object returnedObject) {
if (token == null) {
return returnedObject;
} else {
this.finallyInvocation(token);
if (this.afterInvocationManager != null) {
try {
returnedObject = this.afterInvocationManager.decide(token.getSecurityContext().getAuthentication(), token.getSecureObject(), token.getAttributes(), returnedObject);
} catch (AccessDeniedException var4) {
this.publishEvent(new AuthorizationFailureEvent(token.getSecureObject(), token.getAttributes(), token.getSecurityContext().getAuthentication(), var4));
throw var4;
}
}
return returnedObject;
}
}

