【Spring Security】 注解源码分析
【Spring Security】 注解源码分析
Metadata
title: 【Spring Security】 注解源码分析
date: 2023-02-02 14:28
tags:
- 行动阶段/完成
- 主题场景/组件
- 笔记空间/KnowladgeSpace/ProgramSpace/ModuleSpace
- 细化主题/Module/SpringSecurity
categories:
- SpringSecurity
keywords:
- SpringSecurity
description: 【Spring Security】 注解源码分析
【Spring Security】 注解源码分析
我们通过添加注解的方式,就实现了权限控制。接下来分析下源码,了解他的执行流程。
首先以下面代码问控制入口。
@PreAuthorize("hasRole('ROLE_ROOT')")
public Object test() {
SecurityContext context = SecurityContextHolder.getContext();
Authentication authentication = context.getAuthentication();
MyUser principal = (MyUser) authentication.getPrincipal();
return principal;
}
授权流程图:
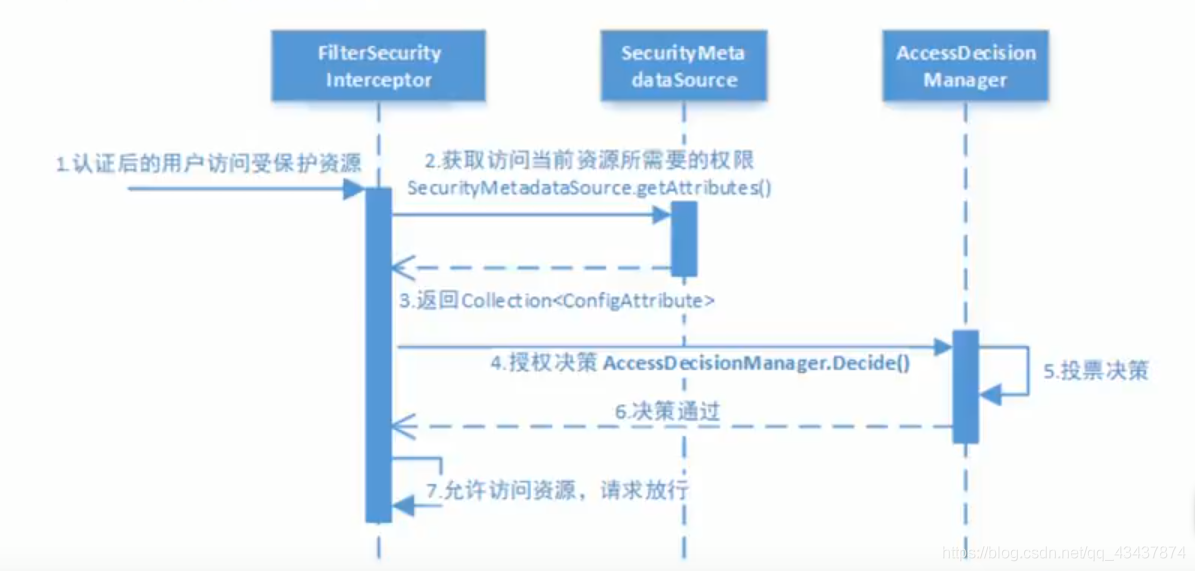
源码分析
核心类
FilterSecurityInterceptor
FilterSecurityInterceptor 作为 Spring Security Filter Chain 的最后一个 Filter,承担着非常重要的作用。如获取当前 request 对应的权限配置,调用访问控制器进行鉴权操作等,都是核心功能。进行访问控制的处理就在这个过滤器中。
ConfigAttribute
ConfigAttribute 是一个接口,其作用为存储相关访问控制的规则。
public interface ConfigAttribute extends Serializable {
String getAttribute();
}
而这些访问规则可以通过配置类或者注解方式来配置。
比如 HttpSecurity 的默认配置为所有的请求都需要被认证,也可以添加自定义的访问控制规则
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
this.logger.debug("Using default configure(HttpSecurity). If subclassed this will potentially override subclass configure(HttpSecurity).");
http.authorizeRequests((requests) -> {
((AuthorizedUrl)requests.anyRequest()).authenticated();
});
http.formLogin();
http.httpBasic();
}
比如可以通过注解方式进行访问控制:
@Secured("IS_AUTHENTICATED_ANONYMOUSLY")
WebExpressionConfigAttribute 是 ConfigAttribute 的常用实现类,并实现了 EvaluationContextPostProcessor 接口,他的主要作用是存储我们配置的表达式及其处理器。
/**
* Simple expression configuration attribute for use in web request authorizations.
*
* @author Luke Taylor
* @since 3.0
* 用于 Web 请求授权的简单表达式配置属性。
*/
class WebExpressionConfigAttribute implements ConfigAttribute, EvaluationContextPostProcessor<FilterInvocation> {
// 表达式 比如
private final Expression authorizeExpression;
// el表达式内容处理处理器
private final EvaluationContextPostProcessor<FilterInvocation> postProcessor;
WebExpressionConfigAttribute(Expression authorizeExpression,
EvaluationContextPostProcessor<FilterInvocation> postProcessor) {
this.authorizeExpression = authorizeExpression;
this.postProcessor = postProcessor;
}
FilterInvocation
FilterInvocation 类,主要是保存与 HTTP 过滤器关联的对象,包括请求、响应、连接器链。
public class FilterInvocation {
static final FilterChain DUMMY_CHAIN = (req, res) -> {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException("Dummy filter chain");
};
private FilterChain chain;
private HttpServletRequest request;
private HttpServletResponse response;
public FilterInvocation(ServletRequest request, ServletResponse response, FilterChain chain) {
Assert.isTrue(request != null && response != null && chain != null, "Cannot pass null values to constructor");
this.request = (HttpServletRequest) request;
this.response = (HttpServletResponse) response;
this.chain = chain;
}
}
InterceptorStatusToken
InterceptorStatusToken 是 FilterSecurityInterceptor 拦截器 beforeInvocation 处理返回的对象,主要包含了反映了安全拦截的状态,最终 afterInvocation 方法会对他进行最终的处理。
public class InterceptorStatusToken {
private SecurityContext securityContext;
private Collection<ConfigAttribute> attr;
private Object secureObject;
private boolean contextHolderRefreshRequired;
public InterceptorStatusToken(SecurityContext securityContext, boolean contextHolderRefreshRequired,
Collection<ConfigAttribute> attributes, Object secureObject) {
this.securityContext = securityContext;
this.contextHolderRefreshRequired = contextHolderRefreshRequired;
this.attr = attributes;
this.secureObject = secureObject;
}
}
RunAsManager
RunAsManager 是一个接口,主要定义了对 Authentication 进行替换的方法。在极少数情况下,用户可以使用不同的 Authentication 替换 SecurityContext 中的 Authentication。
public interface RunAsManager {
Authentication buildRunAs(Authentication authentication, Object object, Collection<ConfigAttribute> attributes);
boolean supports(ConfigAttribute attribute);
boolean supports(Class<?> clazz);
}
AccessDecisionManager
AccessDecisionManager 是访问决策管理器,做出最终的访问控制(授权)决定,他是一个接口,有众多的实现类。每一个具体的实现类可以表示为一种决策。
public interface AccessDecisionManager {
/**
* Resolves an access control decision for the passed parameters.
* @param authentication the caller invoking the method (not null)
* @param object the secured object being called
* @param configAttributes the configuration attributes associated with the secured
* object being invoked
* @throws AccessDeniedException if access is denied as the authentication does not
* hold a required authority or ACL privilege
* @throws InsufficientAuthenticationException if access is denied as the
* authentication does not provide a sufficient level of trust
* 为传递的参数解析访问控制决策
*/
void decide(Authentication authentication, Object object, Collection<ConfigAttribute> configAttributes)
throws AccessDeniedException, InsufficientAuthenticationException;
/**
* Indicates whether this <code>AccessDecisionManager</code> is able to process
* authorization requests presented with the passed <code>ConfigAttribute</code>.
* <p>
* This allows the <code>AbstractSecurityInterceptor</code> to check every
* configuration attribute can be consumed by the configured
* <code>AccessDecisionManager</code> and/or <code>RunAsManager</code> and/or
* <code>AfterInvocationManager</code>.
* </p>
* @param attribute a configuration attribute that has been configured against the
* <code>AbstractSecurityInterceptor</code>
* @return true if this <code>AccessDecisionManager</code> can support the passed
* configuration attribute
* 指示此 <code>AccessDecisionManager</code> 是否能够处理通过传递的 <code>ConfigAttribute</code> 呈现的授权请求
*/
boolean supports(ConfigAttribute attribute);
/**
* Indicates whether the <code>AccessDecisionManager</code> implementation is able to
* provide access control decisions for the indicated secured object type.
* @param clazz the class that is being queried
* @return <code>true</code> if the implementation can process the indicated class
* 指示 <code>AccessDecisionManager</code> 实现是否能够为指示的安全对象类型提供访问控制决策。
*/
boolean supports(Class<?> clazz);
}
AffirmativeBased
AffirmativeBased 是 AccessDecisionManager 默认的实现类,AffirmativeBased 的逻辑是这样的:
(1)只要有AccessDecisionVoter的投票为ACCESS_GRANTED则同意用户进行访问;
(2)如果全部弃权也表示通过;
(3)如果没有一个人投赞成票,但是有人投反对票,则将抛出AccessDeniedException。
public class AffirmativeBased extends AbstractAccessDecisionManager {
public AffirmativeBased(List<AccessDecisionVoter<?>> decisionVoters) {
super(decisionVoters);
}
@Override
@SuppressWarnings({"rawtypes", "unchecked"})
public void decide(Authentication authentication, Object object, Collection<ConfigAttribute> configAttributes)
throws AccessDeniedException {
int deny = 0; // 否决票
// 1. 循环WEB 投票器
for (AccessDecisionVoter voter : getDecisionVoters()) {
// 2. 投票,返回结果
int result = voter.vote(authentication, object, configAttributes);
//
switch (result) {
// 为1 ,表示通过,有一个通过,则直接通过,return退出函数,不抛出异常
case AccessDecisionVoter.ACCESS_GRANTED:
return;
// -1 ,拒绝访问,否决票+1
case AccessDecisionVoter.ACCESS_DENIED:
deny++;
break;
default:
break;
}
}
// 如果否决票》0 抛出AccessDeniedException
if (deny > 0) {
throw new AccessDeniedException(
this.messages.getMessage("AbstractAccessDecisionManager.accessDenied", "Access is denied"));
}
// To get this far, every AccessDecisionVoter abstained
// 3. 没有否决票,也没有赞成票,都弃权了,则检查是否允许如果所有弃权决定。
checkAllowIfAllAbstainDecisions();
}
}
AccessDecisionVoter
AccessDecisionVoter 就表示为投票决策者,也就是一个投票器了。AccessDecisionVoter 是一个接口,定义了三个常量,表示投票结果。
/**
* 访问决策选民, 表示一个类负责对授权决定进行投票
*/
public interface AccessDecisionVoter<S> {
int ACCESS_GRANTED = 1; // 授予访问权限
int ACCESS_ABSTAIN = 0; // 访问弃权
int ACCESS_DENIED = -1; // 拒绝访问
boolean supports(ConfigAttribute attribute);
boolean supports(Class<?> clazz);
// 投票
int vote(Authentication authentication, S object, Collection<ConfigAttribute> attributes);
}
WebExpressionVoter
AccessDecisionManager 默认的投票器 WebExpressionVoter。其实,就是对使用 http.authorizeRequests() 基于 Spring-EL 进行控制权限的的授权决策类。
/**
* Voter which handles web authorisation decisions.
*
* @author Luke Taylor
* @since 3.0
* 处理web授权决定的选民
*/
public class WebExpressionVoter implements AccessDecisionVoter<FilterInvocation> {
private final Log logger = LogFactory.getLog(getClass());
// 默认的WebSecurity授权表达式处理器
private SecurityExpressionHandler<FilterInvocation> expressionHandler = new DefaultWebSecurityExpressionHandler();
// 投票
@Override
public int vote(Authentication authentication, FilterInvocation filterInvocation,
Collection<ConfigAttribute> attributes) {
// 1. 校验参数
Assert.notNull(authentication, "authentication must not be null");
Assert.notNull(filterInvocation, "filterInvocation must not be null");
Assert.notNull(attributes, "attributes must not be null");
// 2. 获取http配置项
WebExpressionConfigAttribute webExpressionConfigAttribute = findConfigAttribute(attributes);
// 3. 没有配置规则,弃权
if (webExpressionConfigAttribute == null) {
this.logger
.trace("Abstained since did not find a config attribute of instance WebExpressionConfigAttribute");
return ACCESS_ABSTAIN;
}
// 4. 对EL表达式进行处理
EvaluationContext ctx = webExpressionConfigAttribute.postProcess(
this.expressionHandler.createEvaluationContext(authentication, filterInvocation), filterInvocation);
boolean granted = ExpressionUtils.evaluateAsBoolean(webExpressionConfigAttribute.getAuthorizeExpression(), ctx);
if (granted) {
// 5. 符合条件,赞成票
return ACCESS_GRANTED;
}
this.logger.trace("Voted to deny authorization");
// 6. 最后都没有则反对票
return ACCESS_DENIED;
}
private WebExpressionConfigAttribute findConfigAttribute(Collection<ConfigAttribute> attributes) {
for (ConfigAttribute attribute : attributes) {
if (attribute instanceof WebExpressionConfigAttribute) {
return (WebExpressionConfigAttribute) attribute;
}
}
return null;
}
@Override
public boolean supports(ConfigAttribute attribute) {
return attribute instanceof WebExpressionConfigAttribute;
}
@Override
public boolean supports(Class<?> clazz) {
return FilterInvocation.class.isAssignableFrom(clazz);
}
public void setExpressionHandler(SecurityExpressionHandler<FilterInvocation> expressionHandler) {
this.expressionHandler = expressionHandler;
}
}
SecurityExpressionHandler
Web 安全表达式处理器 (handler)。最后对 EL 访问控制表达式的处理,都是在此接口中的实现类进行。它的默认实现类为 DefaultWebSecurityExpressionHandler。这个类的主要作用是创建 SecurityExpressionRoot 对象。
public class DefaultWebSecurityExpressionHandler extends AbstractSecurityExpressionHandler<FilterInvocation>
implements SecurityExpressionHandler<FilterInvocation> {
private AuthenticationTrustResolver trustResolver = new AuthenticationTrustResolverImpl();
// 角色前缀
private String defaultRolePrefix = "ROLE_";
@Override
protected SecurityExpressionOperations createSecurityExpressionRoot(Authentication authentication,
FilterInvocation fi) {
WebSecurityExpressionRoot root = new WebSecurityExpressionRoot(authentication, fi);
root.setPermissionEvaluator(getPermissionEvaluator());
root.setTrustResolver(this.trustResolver);
root.setRoleHierarchy(getRoleHierarchy());
root.setDefaultRolePrefix(this.defaultRolePrefix);
return root;
}
}
WebSecurityExpressionRoot
WebSecurityExpressionRoot 实现了 SecurityExpressionRoot 接口,其顶级接口为 SecurityExpressionOperations。
SecurityExpressionOperations 接口中定义个很多方法,每个方法都关联着一个访问控制表达式。
/**
* Standard interface for expression root objects used with expression-based security.
*
* @author Andrei Stefan
* @author Luke Taylor
* @since 3.1.1
* 与基于表达式的安全性一起使用的表达式根对象的标准接口
*/
public interface SecurityExpressionOperations {
/**
* Gets the {@link Authentication} used for evaluating the expressions
* @return the {@link Authentication} for evaluating the expressions
*/
Authentication getAuthentication();
/**
* Determines if the {@link #getAuthentication()} has a particular authority within
* {@link Authentication#getAuthorities()}.
* @param authority the authority to test (i.e. "ROLE_USER")
* @return true if the authority is found, else false
*/
boolean hasAuthority(String authority);
/**
* Determines if the {@link #getAuthentication()} has any of the specified authorities
* within {@link Authentication#getAuthorities()}.
* @param authorities the authorities to test (i.e. "ROLE_USER", "ROLE_ADMIN")
* @return true if any of the authorities is found, else false
*/
boolean hasAnyAuthority(String... authorities);
/**
* <p>
* Determines if the {@link #getAuthentication()} has a particular authority within
* {@link Authentication#getAuthorities()}.
* </p>
* <p>
* This is similar to {@link #hasAuthority(String)} except that this method implies
* that the String passed in is a role. For example, if "USER" is passed in the
* implementation may convert it to use "ROLE_USER" instead. The way in which the role
* is converted may depend on the implementation settings.
* </p>
* @param role the authority to test (i.e. "USER")
* @return true if the authority is found, else false
*/
boolean hasRole(String role);
/**
* <p>
* Determines if the {@link #getAuthentication()} has any of the specified authorities
* within {@link Authentication#getAuthorities()}.
* </p>
* <p>
* This is a similar to hasAnyAuthority except that this method implies that the
* String passed in is a role. For example, if "USER" is passed in the implementation
* may convert it to use "ROLE_USER" instead. The way in which the role is converted
* may depend on the implementation settings.
* </p>
* @param roles the authorities to test (i.e. "USER", "ADMIN")
* @return true if any of the authorities is found, else false
*/
boolean hasAnyRole(String... roles);
/**
* Always grants access.
* @return true
*/
boolean permitAll();
/**
* Always denies access
* @return false
*/
boolean denyAll();
/**
* Determines if the {@link #getAuthentication()} is anonymous
* @return true if the user is anonymous, else false
*/
boolean isAnonymous();
/**
* Determines ifthe {@link #getAuthentication()} is authenticated
* @return true if the {@link #getAuthentication()} is authenticated, else false
*/
boolean isAuthenticated();
/**
* Determines if the {@link #getAuthentication()} was authenticated using remember me
* @return true if the {@link #getAuthentication()} authenticated using remember me,
* else false
*/
boolean isRememberMe();
/**
* Determines if the {@link #getAuthentication()} authenticated without the use of
* remember me
* @return true if the {@link #getAuthentication()} authenticated without the use of
* remember me, else false
*/
boolean isFullyAuthenticated();
/**
* Determines if the {@link #getAuthentication()} has permission to access the target
* given the permission
* @param target the target domain object to check permission on
* @param permission the permission to check on the domain object (i.e. "read",
* "write", etc).
* @return true if permission is granted to the {@link #getAuthentication()}, else
* false
*/
boolean hasPermission(Object target, Object permission);
/**
* Determines if the {@link #getAuthentication()} has permission to access the domain
* object with a given id, type, and permission.
* @param targetId the identifier of the domain object to determine access
* @param targetType the type (i.e. com.example.domain.Message)
* @param permission the perission to check on the domain object (i.e. "read",
* "write", etc)
* @return true if permission is granted to the {@link #getAuthentication()}, else
* false
*/
boolean hasPermission(Object targetId, String targetType, Object permission);
}
WebSecurityExpressionRoot 可以理解为权限表达式对应的 JAVA 类,他除了接口中的表达式支持,还添加了一个 hasIpAddress 方法,可以对 IP 进行控制。
public class WebSecurityExpressionRoot extends SecurityExpressionRoot {
/**
* Allows direct access to the request object
*/
public final HttpServletRequest request;
public WebSecurityExpressionRoot(Authentication a, FilterInvocation fi) {
super(a);
this.request = fi.getRequest();
}
/**
* Takes a specific IP address or a range using the IP/Netmask (e.g. 192.168.1.0/24 or
* 202.24.0.0/14).
* @param ipAddress the address or range of addresses from which the request must
* come.
* @return true if the IP address of the current request is in the required range.
*/
public boolean hasIpAddress(String ipAddress) {
IpAddressMatcher matcher = new IpAddressMatcher(ipAddress);
return matcher.matches(this.request);
}
}

